Arcade: Tide Rhythm Machine
Project description
Arcade is a project about the development of the "Tide Rhythm Machine", an educational game machine designed to illustrate the differences between analog and digital computing, while promoting collaborative play.


It's design pays homage to William Thomson's 'Tide Prediction Machine', a notable analog computer used for forecasting tides in coastal areas.
In this cooperative rhythm game, players will experience both analog and digital computations side by side, aimed to illustrate the characteristics of both while working together to achieve a high score.
Analog vs Digital
But what are the difference between analog and digital computing?
Analog
- Continuous
- Quantities of interest are represented by physical parameters
- Energy efficient
- Single purpose
- Non-repeatable
- Inexact (~ 1% error rate)
Digital
- Discrete
- Quantities of interest are represented by symbols
- Relatively energy inefficient
- Universal
- Repeatable
- Exact
Gameplay
The game is based on a co-pp rhythm game mechanic with the goal to reach a high score. It goes faster the longer you survive.
The Digital Player, has to hit notes falling down at the right timing. If they miss, they lose a Health Point. If all Health Points are lost, the game ends.
The Analog Player, has to catch the falling Pinballs, in order to reduce the speed -> making it easier to predict the notes for the other player.
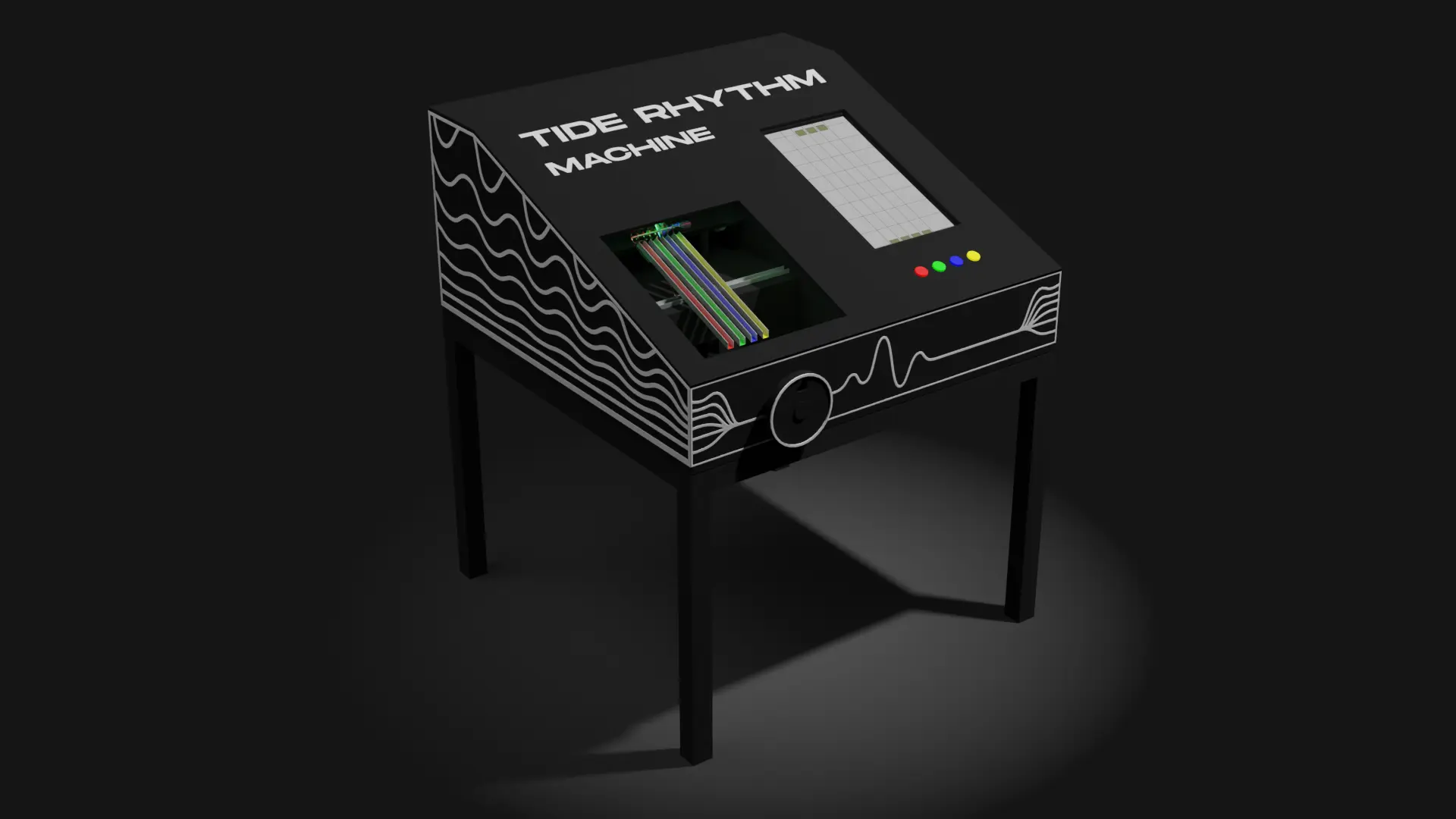
Components
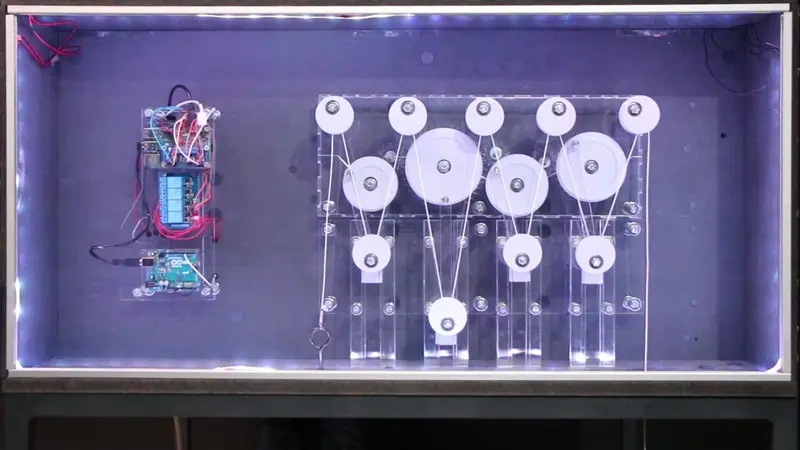
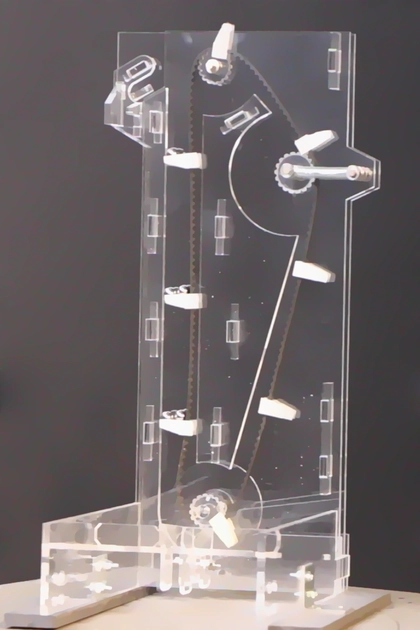
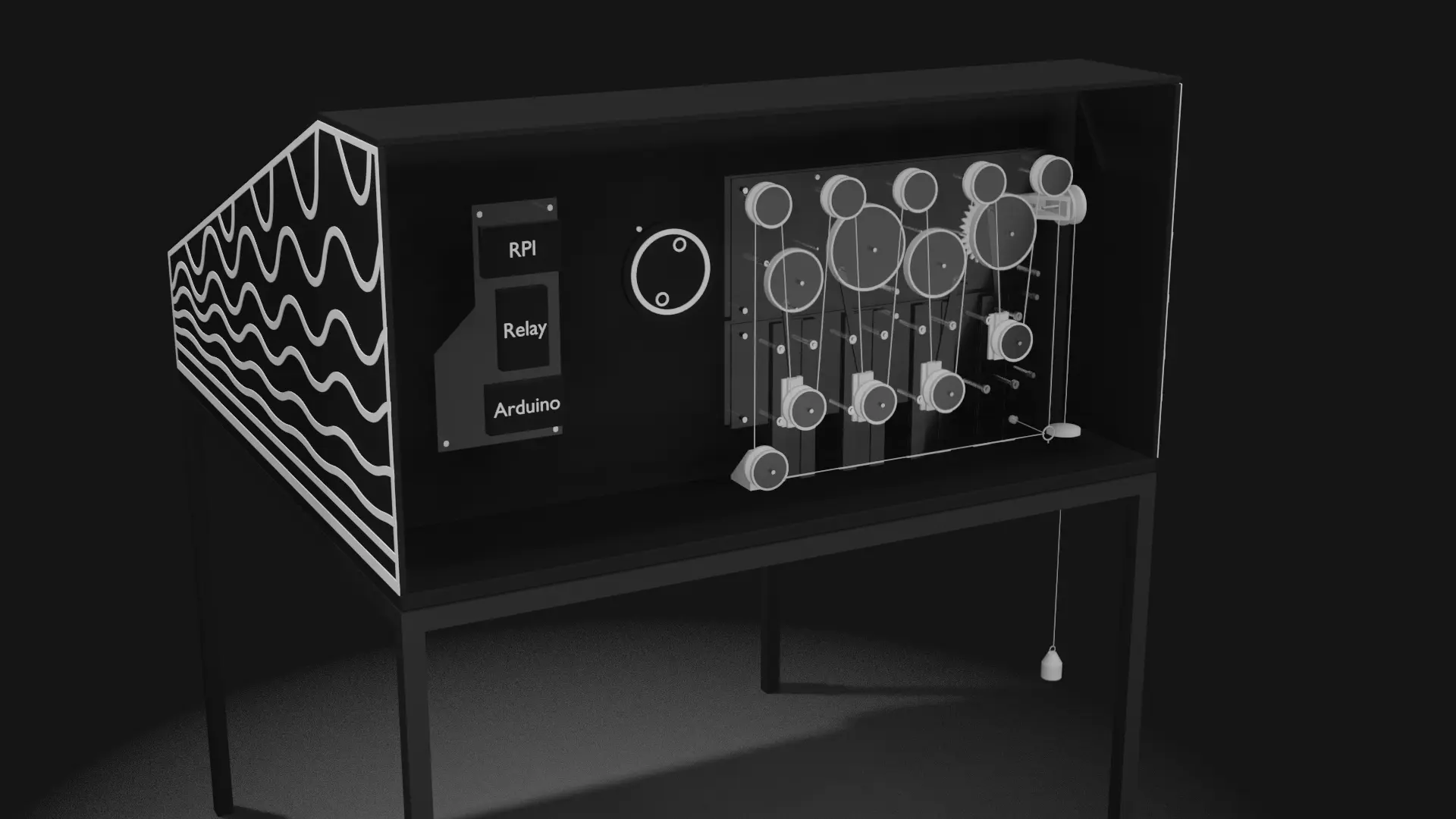
Analog Computer
This is main piece of the machine, the analog computer. 4 crank shafts are drawing a curve e.g tides that can than be translated into movement and speed for the game.
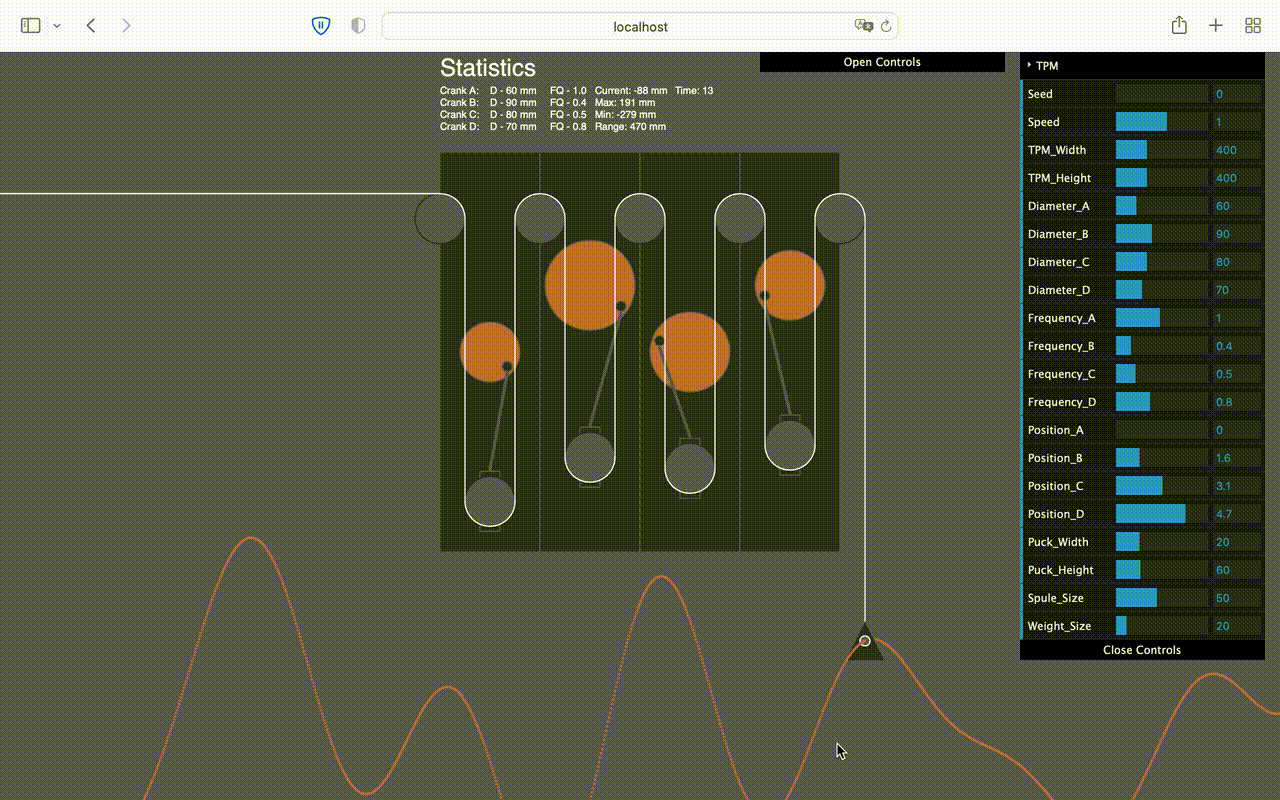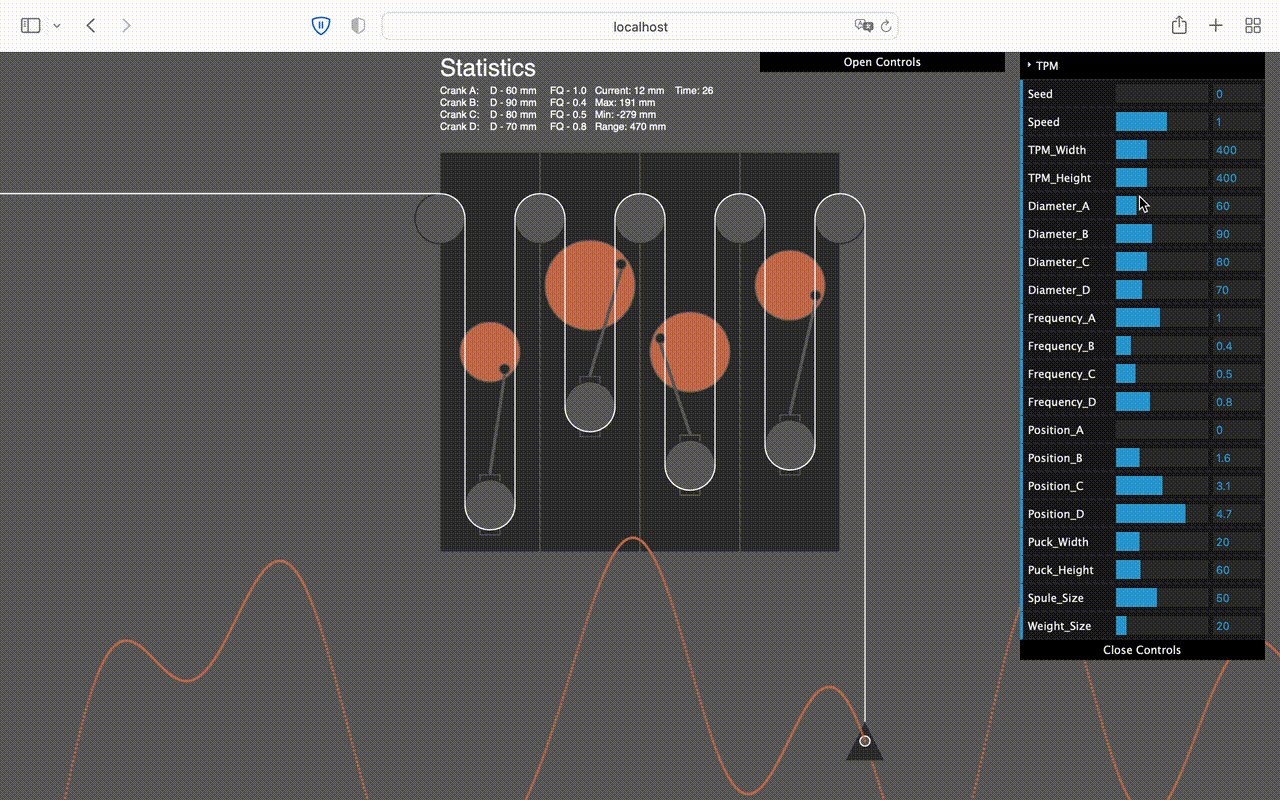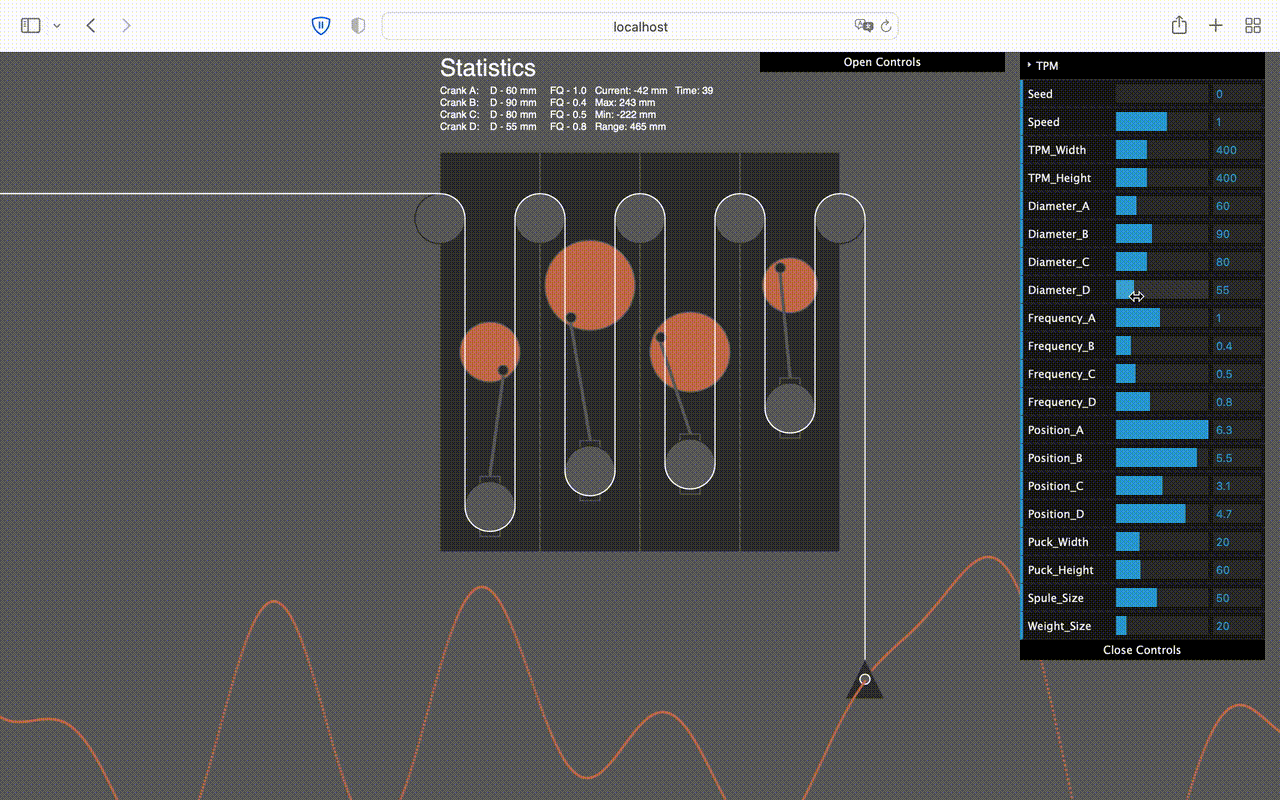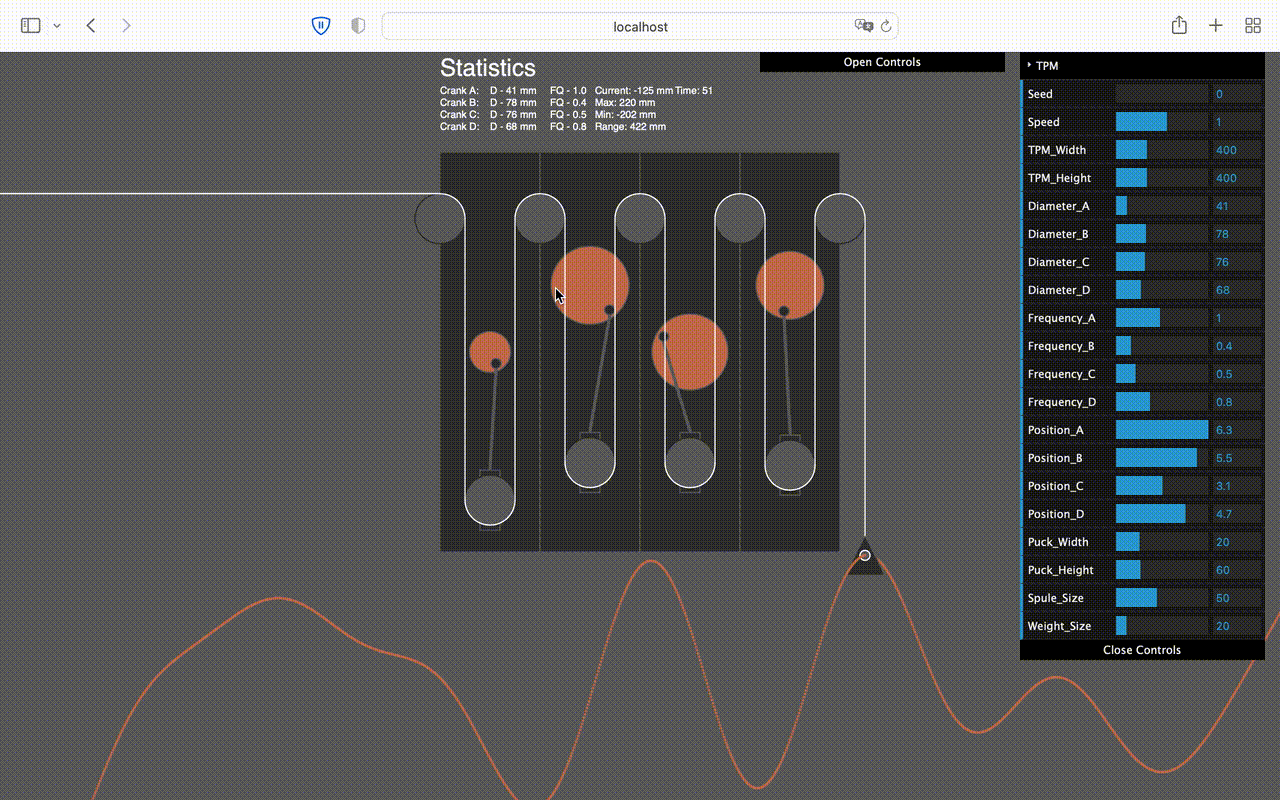
Callibration Tool
In order to callibrate the computer, I've coded a tool in 'Processing' to calculate the movement the machine will make according to how it is adjusted.
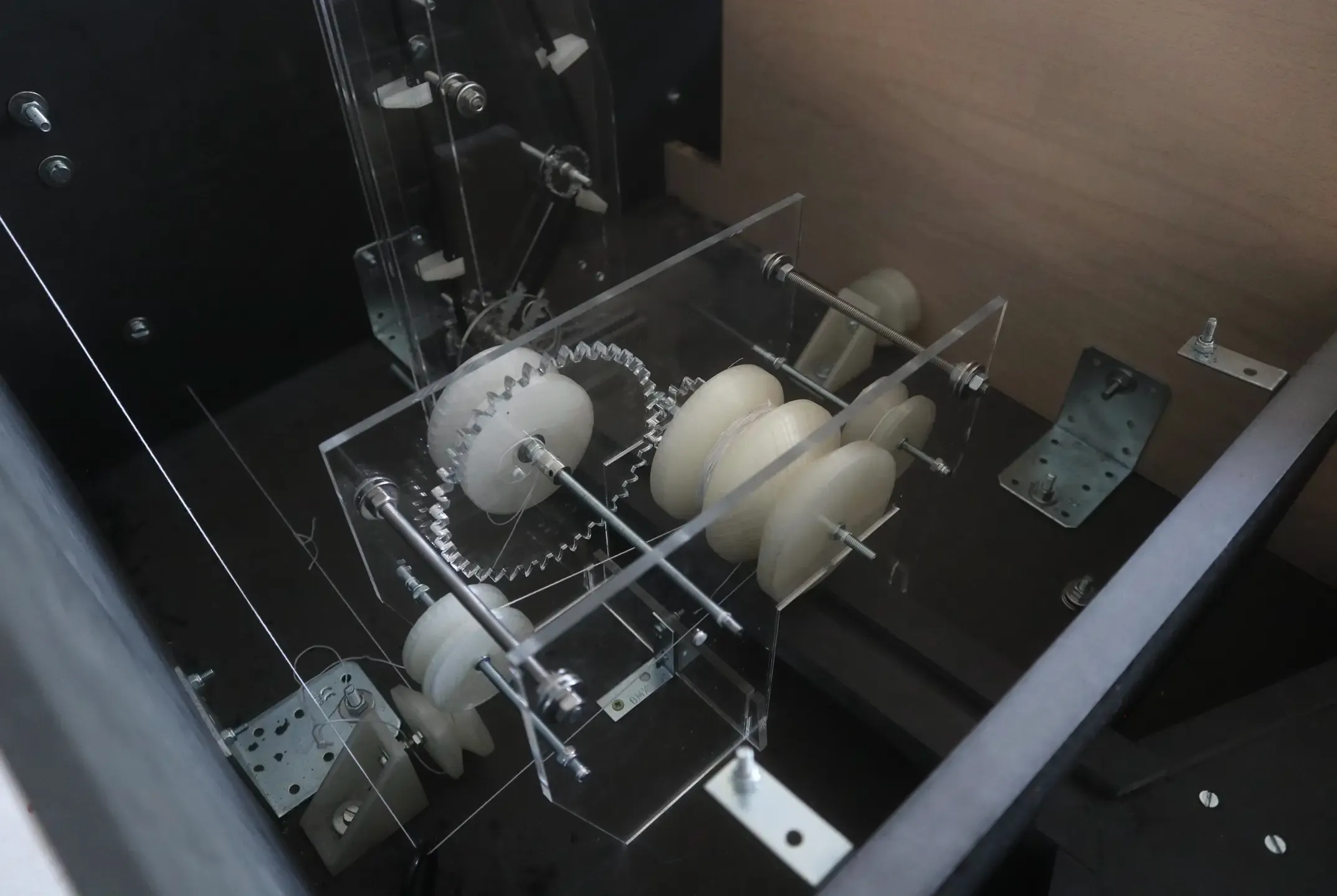
Gearbox
The gearbox then translates the calculations from the analog computer into one axis.
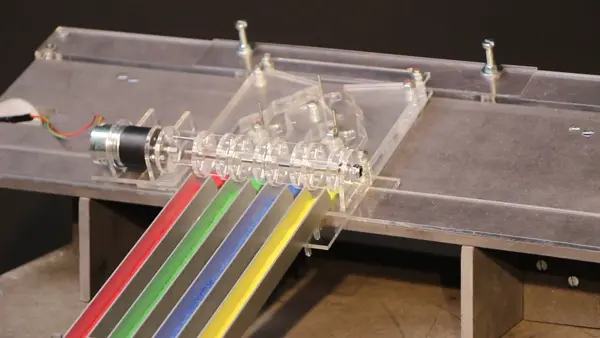
Pinball Distributer
Pinballs are then evenly split to the 4 lanes and let go in tact of the rythm game. The lanes are swaying according to the 'tides' predicted by the analog computer.
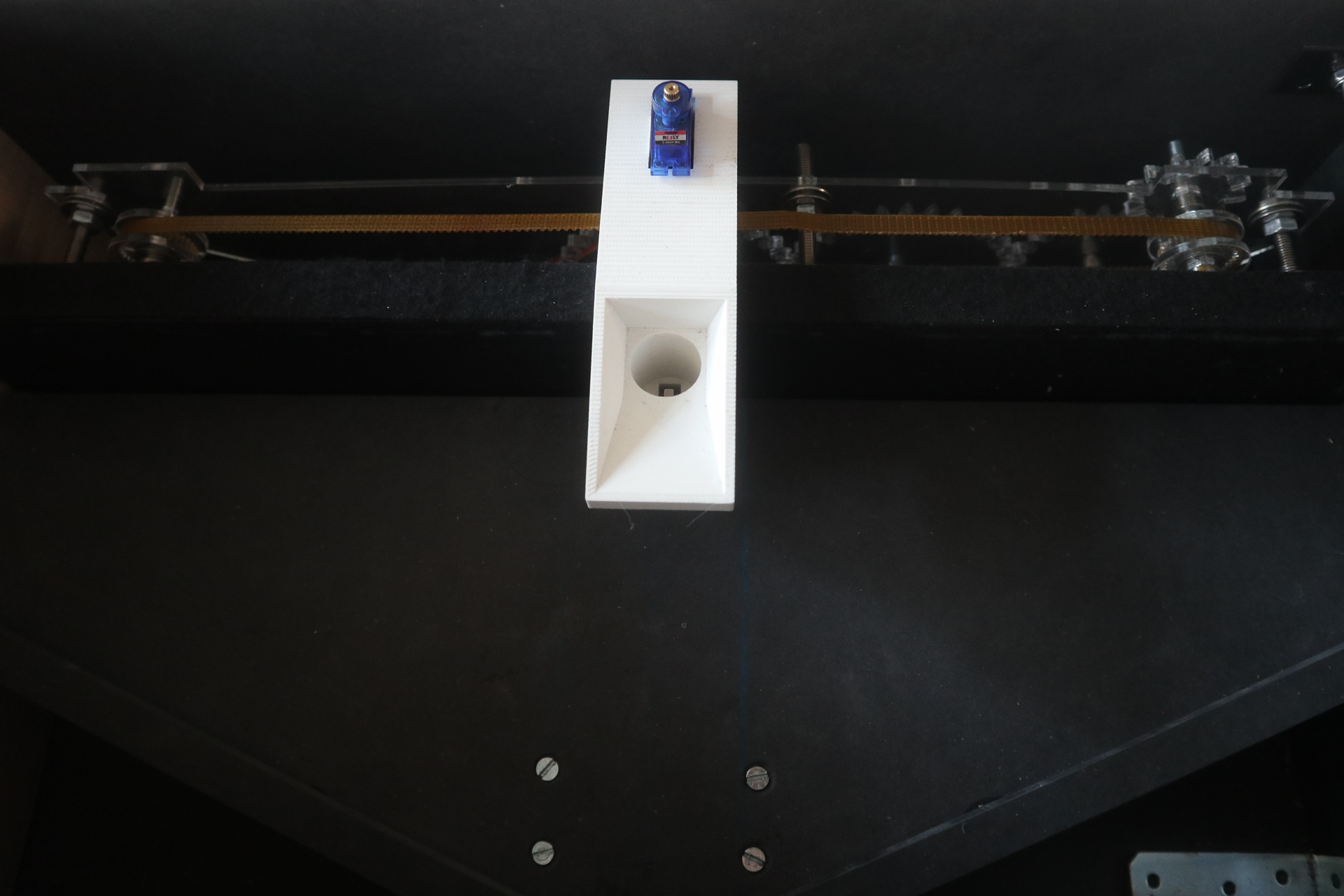
Pinball Catcher
The pinballs have to be caught by the Analog player with the catcher.
Pinball Lift
Pinballs are than lifted back up to the distributer, completing the cycle.
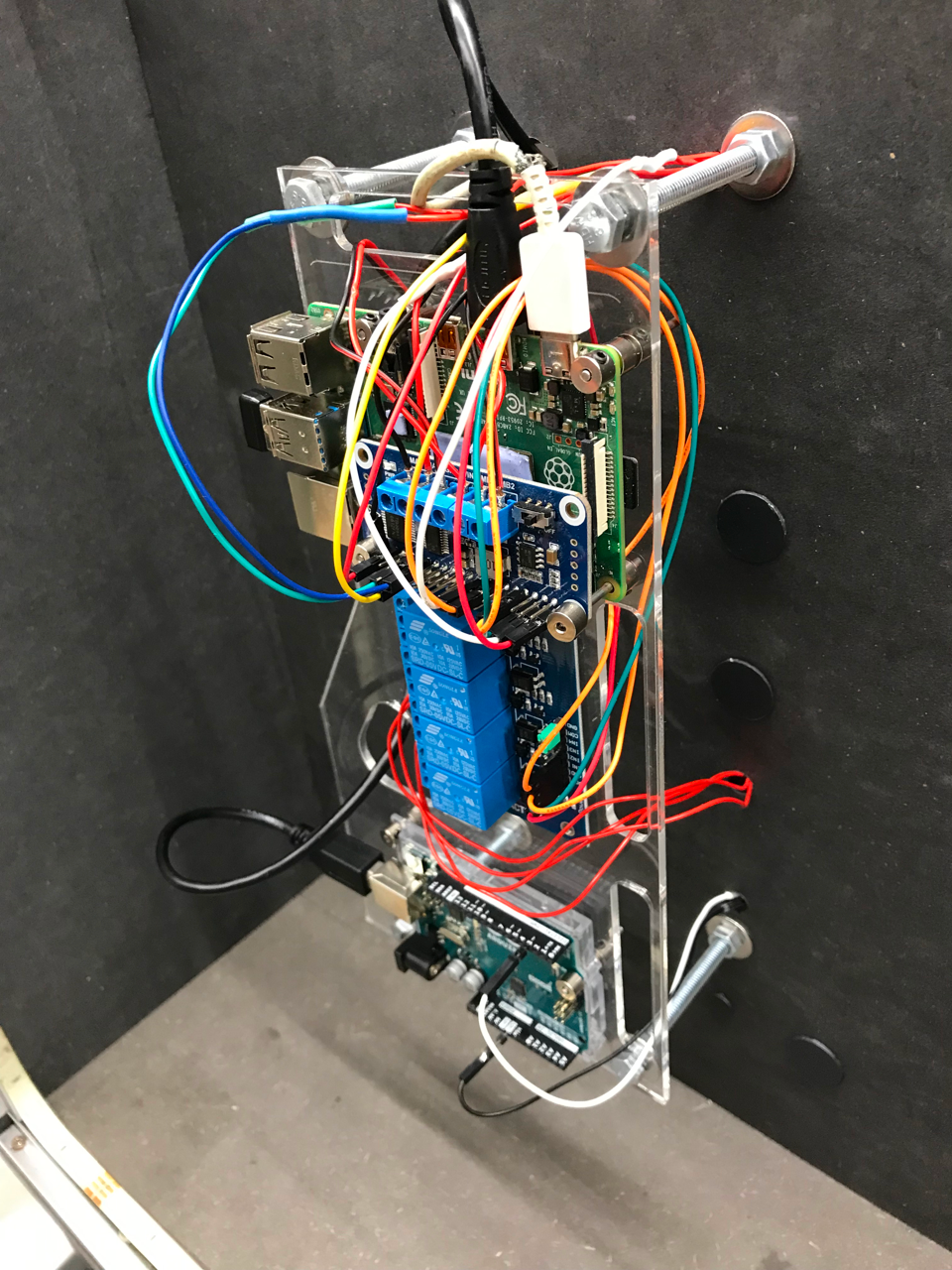
Digital Computer
On the other side, the digital computer runs the digital counter part, registering the points gained during the play.
Digital Gameplay
Points are gained by pressing the buttons at the right frame.

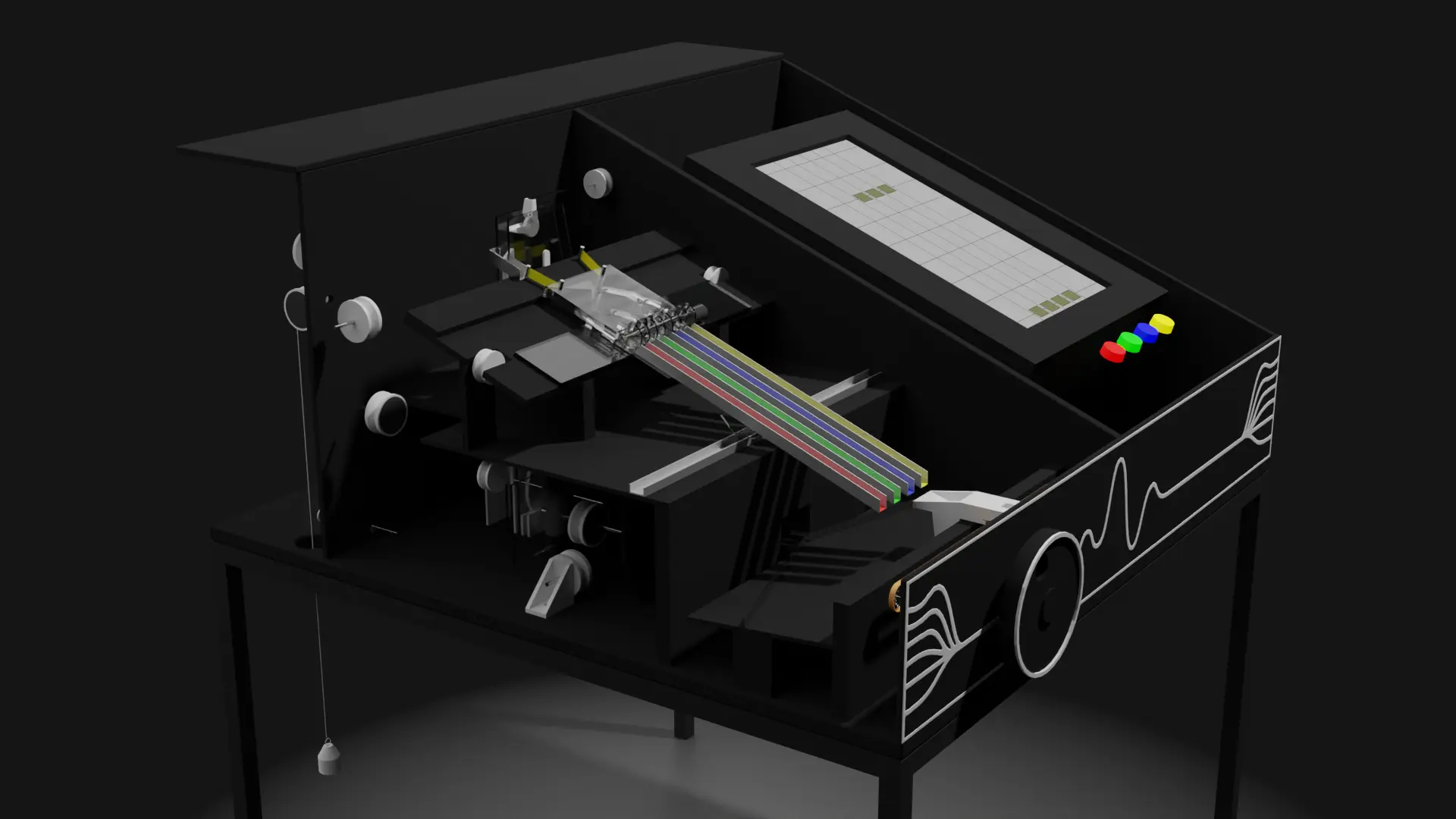
3D Visualization


Gallery
Special Thanks:
Department of Design Investigations
Exhibited at:
Angewandte Festival, 2022 (AT)